A crossflow turbine has multiple splits that are inconsistently and longitudinally arranged around the flow cylinder and glued to the inlet and outlet edges of the water to create effective flow. The tip of the blade closes like an old water wheel, giving the turbine a “hamster cage.”
Crossflow turbines have two independent nozzles; their angle is set at 45 degrees, the water is positioned at the best angle on the blades. The moving force generates the potential energy of the water. The flow of water controls through an adjustment mechanism during rotation to increase or decrease the transmission of the nozzle while controlling the power. These turbines have lower efficiency than the Kaplan turbines.
Working of Crossflow Turbine
In the cross-flow turbine, the water enters in the form of a flat plate rather than a circular jet, such as a Pelton turbine. The water plate is guided to the turbine blades by the inlet drive vanes and ensures that the water hits the blades at the right angle for maximum efficiency.
Water passes through the blades and causes torque on these blades. After reaching the blade, the veil of water passes through the turbine, and when it comes out, it hits the blade again and creates more torque.
The first hit of water on the blade creates more force than the second hit. Since this type of turbine uses a jet of water to generate impulses in the turbine, the cross-flow turbine is a type of impulse turbine, similar to the Pelton turbine.
Components of Crossflow Turbine
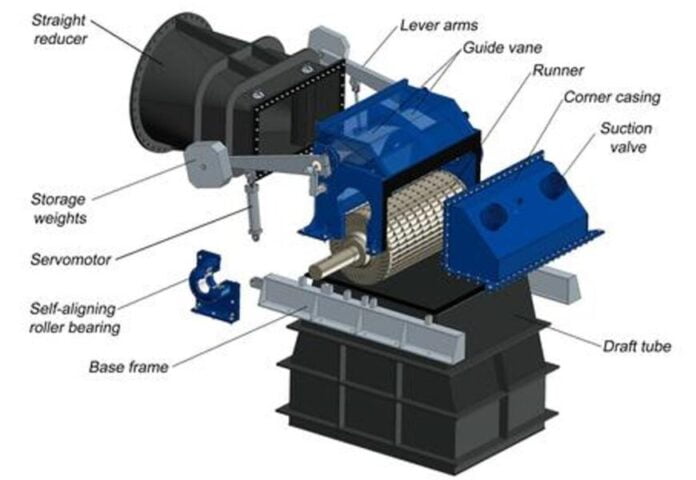
The crossflow turbine has the following major parts:
1) Turbine Casing
The casing of the crossflow turbine is made of structural steel. It is stable and durable. It has resistant to shock and cold. If the abrasive content of the water is high (such as sand, silt) or if the actual composition of the corrosive water (such as seawater, acidic water) is considered, all the water-related components of the turbine are made of stainless steel.
2) Guide vanes
In split-type cross-flow turbines, the working water is driven by two force-balanced contour vanes. The jet blade splits the water, balances it, and allows it to enter the channel slowly, regardless of the width of the unit. Two rotating guides blades are mounted exactly in the turbine casing and can be used as a means to close the turbine if the height is low. This eliminates the need for a shut-off valve between the pressure line and the turbine. Both pickups are equipped with independent sliding arms connected to automatic or manual control. The driving vanes are mounted on heavy-duty bearings without any maintenance. If the turbine is closed, it can be closed by gravity and increase the weight of the boom end.
3) Runner
The runner is the most important part of the turbine. It features polished and ironed steel blades made with proven techniques. Based on real hydraulic data, structural steel or stainless steel is used for its structure.
Check out: What Is a Reciprocating Compressor? Pros & Cons
The two ends of the blades are mounted on a rotating plate and rotated according to a special procedure in the central disc of the plate. Depending on the size, the runner has a maximum of 37 blades. Straight, slanted blades create only a small axial force, so power bearings with complex installation and lubrication are not required. Multiple discs support the widest lane blades. Before finally installing the turbine, carefully balance the impeller and check for cracks.
4) Bearings
Crossflow turbines are equipped with self-aligning bearings, which have many advantages, including low roller resistance and easy maintenance. Bearing casing design prevents water from entering the bearing and lubricating contact with working water. This basic quality is recorded in the design of the cross-flow turbine casing. In addition, the rotor is centered in the turbine casing by the bearing. The creative technical solution produces maintenance-free sealing elements. Apart from the annual grease change, the bearings require no maintenance. Furthermore, the technical solution used makes it possible to easily replace the impeller without having to move the entire turbine into position.
3) Draft tube
A Crossflow turbine is a non-flow turbine, like Pelton turtles. But in the case of medium or low door leaves, you can use an exhaust pipe to use the whole door. However, the water column in the suction pipe must be checked. This is ensured by the adjustment of the air valve, which affects the suction pressure in the turbine casing. In this way, it is possible to use turbines with a suction height of 1 to 3 meters without any risk of creating holes.
Advantages of Crossflow Turbines
- They have good regulations.
- They have a low cost.
- These turbines don’t require high maintenance.
- These turbines have the capability to remove small debris from the runner.
Disadvantages of the Crossflow Turbine
- A crossflow turbine has lower efficiency than other turbines such as Kaplan turbine and Pelton Wheel turbine.
- It has self-starting issues.